skip to main |
skip to sidebar
To display a dialog, you first override the onCreateDialog() method in the Activity class
The onCreateDialog() method is a callback for creating dialogs that are managed by the activity. When you call the showDialog() method, this callback will be invoked. The showDialog() method accepts an integer argument identifying a particular dialog to display.
Hiển thị các bài đăng có nhãn share code. Hiển thị tất cả bài đăng
Hiển thị các bài đăng có nhãn share code. Hiển thị tất cả bài đăng
Thứ Tư, 2 tháng 12, 2015
Thứ Bảy, 31 tháng 10, 2015
Using android Camera surfaceView android studio
1. Create a New Android Application Project
2. Creating the layout of the main
We are going to make a very simple layout xml for the CameraDemo
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/btn_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/layout_area"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:background="#000">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/btn_flash"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:padding="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_action_flash_off" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/btn_switch"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:padding="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_action_switch_camera" />
</RelativeLayout>
<SurfaceView
android:id="@+id/surfaceView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_above="@+id/layout_area1"
android:layout_below="@+id/layout_area" />
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/layout_area1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="#000">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/btn_exit"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_action_remove" />
<com.melnykov.fab.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/btn_take_photo"
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_action_camera" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/btn_lib"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_library_cam" />
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
</FrameLayout>
3. Creating the source code
package com.example.tb_laota.camerademo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.hardware.Camera.PictureCallback;
import android.hardware.Camera.ShutterCallback;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.melnykov.fab.FloatingActionButton;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import butterknife.ButterKnife;
import butterknife.InjectView;
/**
* Created by tb_laota on 10/30/2015.
*/
public class CameraActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
Camera camera;
@InjectView(R.id.surfaceView)
SurfaceView surfaceView;
@InjectView(R.id.btn_take_photo)
FloatingActionButton btn_take_photo;
SurfaceHolder surfaceHolder;
PictureCallback jpegCallback;
ShutterCallback shutterCallback;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.camera_activity);
ButterKnife.inject(this);
surfaceHolder = surfaceView.getHolder();
// Install a surfaceHolder.Callback so we get notified when the
// underlying surface is created and destroyed.
surfaceHolder.addCallback(this);
//deprecated setting, but required on android versions prior to 3.0
surfaceHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
btn_take_photo.setOnClickListener(new FloatingActionButton.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
captureImage();
}
});
jpegCallback = new PictureCallback() {
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] data, Camera camera) {
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
File file_image = getDirc();
if (!file_image.exists() && !file_image.mkdirs()) {
Toast.makeText(getApplication(), "Can't create directory to save image", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyymmddhhmmss");
String date = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
String photofile = "Cam_Demo" + date + ".jpg";
String file_name = file_image.getPath() + File.separator + photofile;
File picfile = new File(file_name);
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(picfile);
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
} catch (IOException ex) {
} finally {
}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Picture saved", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
refreshCamera();
refreshGallery(picfile);
}
};
}
//refresh gallery
public void refreshGallery(File file) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_FILE);
intent.setData(Uri.fromFile(file));
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
public void refreshCamera() {
if (surfaceHolder.getSurface() == null) {
//preview surface does not exist
return;
}
//stop preview before making changes
try {
camera.stopPreview();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
//set preview size and make any resize, rotate or
//reformatting changes here
//start preview with new settings
try {
camera.setPreviewDisplay(surfaceHolder);
camera.startPreview();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
public File getDirc() {
File dics = Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_DCIM);
return new File(dics, "Camera_Demo");
}
public void captureImage() {
//take the picture
camera.takePicture(null, null, jpegCallback);
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
//open the camera
try {
camera = Camera.open();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
}
Camera.Parameters parameters;
parameters = camera.getParameters();
//modify parameter
parameters.setPreviewFrameRate(20);
parameters.setPreviewSize(352, 288);
camera.setParameters(parameters);
camera.setDisplayOrientation(90);
try {
//The surface thas been created, now tell the camera where to draw
//the preview
camera.setPreviewDisplay(surfaceHolder);
camera.startPreview();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) {
refreshCamera();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
//stop preview and release camera
camera.stopPreview();
camera.release();
camera = null;
}
}
In these lines, we find our SurfaceView from our main layout and we get a holder, an abstract interface to someone holding a display surface. This, allows us to control the surface size and format, edit the pixels in the surface, and monitor changes to the surface. We also install a SurfaceHolder.Callback so we get notified when the underlying surface is created and destroyed. We have also written the surfaceHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS); deprecated setting, but required on Android versions prior to 3.0.
4. Android Manifest
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.tb_laota.camerademo">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.autofocus" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".CameraActivity"></activity>
</application>
</manifest>
5. Build, compile and run
Thứ Năm, 10 tháng 9, 2015
Android - XML Parser Tutorial use of XMLPullParser parse xml on web api|android studio
XML stands for Extensible Mark-up Language.XML is a very popular format and commonly used for sharing data on the internet. This chapter explains how to parse the XML file and extract necessary information from it.
XML-Parsing
we will create XMLPullParser object , but in order to create that we will first create XmlPullParserFactory object and then call its newPullParser() method to create XMLPullParser
Example:
Here is an example demonstrating the use of XMLPullParser class. It creates a basic Weather application that allows you to parse XML from google weather api and show the result.
Following is the content of the modified main activity file MainActivity.java.
package androiddemo.example.duyhoang.xmlparsedemo; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private EditText txt1, txt2, txt3, txt4, txt5; private String url1 = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q="; private String url2 = "&mode=xml"; private HandleXml obj; Button btnWeather; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btnWeather = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_weather); txt1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txtLocation); txt2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txt_curency); txt3 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txt_temp); txt4 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txt_humidity); txt5 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txt_pressure); btnWeather.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { String url = txt1.getText().toString(); String finalUrl = url1 + url + url2; txt2.setText(finalUrl); obj = new HandleXml(finalUrl); obj.fetchXML(); while (obj.parsingComplete) ; txt2.setText(obj.getCountry()); txt3.setText(obj.getTemperature()); txt4.setText(obj.getHumidity()); txt5.setText(obj.getPressure()); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }
Following is the content of src/com.example.xmlparser/HandleXML.java.
package androiddemo.example.duyhoang.xmlparsedemo; import android.util.Xml; import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser; import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserFactory; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URL; /** * Created by DUYHOANG on 9/10/2015. */public class HandleXml { private String country = "country"; private String temperature = "temperature"; private String humidity = "humidity"; private String pressure = "pressure"; private String urlString = null; private XmlPullParserFactory xmlFactoryObject; public volatile boolean parsingComplete = true; public HandleXml(String url) { this.urlString = url; } public String getCountry() { return country; } public String getTemperature() { return temperature; } public String getHumidity() { return humidity; } public String getPressure() { return pressure; } public void parseXMLAndStorelt(XmlPullParser myParser) { int event; String text = null; try { event = myParser.getEventType(); while (event != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { String name = myParser.getName(); switch (event) { case XmlPullParser.START_TAG: break; case XmlPullParser.TEXT: text = myParser.getText(); break; case XmlPullParser.END_TAG: if (name.equals("country")) { country = text; } else if (name.equals("humidity")) { humidity = myParser.getAttributeValue(null, "value"); } else if (name.equals("pressure")) { pressure = myParser.getAttributeValue(null, "value"); } else if (name.equals("temperature")) { temperature = myParser.getAttributeValue(null, "value"); } else { } break; } event = myParser.next(); } parsingComplete = false; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void fetchXML() { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { URL url = new URL(urlString); HttpURLConnection connect = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); connect.setReadTimeout(10000); connect.setConnectTimeout(15000); connect.setRequestMethod("GET"); connect.setDoInput(true); connect.connect(); InputStream stream = connect.getInputStream(); xmlFactoryObject = XmlPullParserFactory.newInstance(); XmlPullParser myparser = xmlFactoryObject.newPullParser(); myparser.setFeature(XmlPullParser.FEATURE_PROCESS_NAMESPACES, false); myparser.setInput(stream, null); parseXMLAndStorelt(myparser); stream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); thread.start(); } }Following is the modified content of the xml res/layout/activity_main.xml.<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="@string/fetch" android:textSize="30dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/textView1" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:gravity="center" android:text="@string/weather_report" android:textColor="@color/text_color" android:textSize="30dp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtLocation" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/textView2" android:hint="@string/Location" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_weather" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/txtLocation" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="@string/weather" /> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/linearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/btn_weather" android:orientation="vertical"> <EditText android:id="@+id/txt_curency" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/curency" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txt_temp" android:text="@string/temp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txt_humidity" android:text="@string/humidity" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txt_pressure" android:text="@string/pressure" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>Following is the content of AndroidManifest.xml file.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="androiddemo.example.duyhoang.xmlparsedemo" > <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>Thank's for watching. good luck!!!
Thứ Bảy, 4 tháng 7, 2015
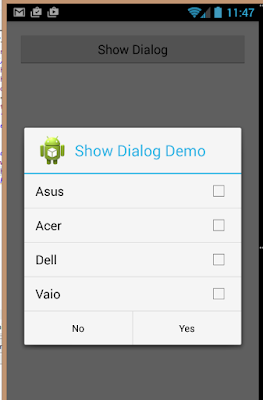
Displaying a dialog using an activity in android tutorial
Displaying a dialog using an activity in android tutorial.
There are times where you need to display a dialog window to get a confirmation from the user. In
this case, you can override the onCreateDialog()protected method defined in the base Activity
class to display a dialog window. The following Try It Out shows you how.
Now, create a new android project.
Edit interface in activity_main.xml file:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.example.demoshowdialog.MainActivity"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnShow_Dialog"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Show Dialog" />
</RelativeLayout>
Next, the proccess code in MainActivity.java file:
import android.app.Activity;
import
android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.Dialog;
import
android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import
android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import
android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button btnShow_Dialog;
CharSequence[] items = { "Asus", "Acer", "Dell", "Vaio" };
boolean[] bool = new boolean[items.length];
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btnShow_Dialog = (Button)
findViewById(R.id.btnShow_Dialog);
btnShow_Dialog.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showDialog(0);
}
});
}
@Override
protected Dialog
onCreateDialog(int id) {
// TODO Auto-generated
method stub
switch (id) {
case 0:
return new AlertDialog.Builder(this)
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setTitle("Show Dialog
Demo")
.setPositiveButton("Yes",new
DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void
onClick(DialogInterface dialog,int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated
method stub
}
})
.setNegativeButton("No",new
DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void
onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated
method stub
}
})
.setMultiChoiceItems(items, bool,new
DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void
onClick(DialogInterface dialog,int which, boolean isChecked) {
// TODO Auto-generated
method stub
}
}).create();
}
return null;
}
}
Explain:To display a dialog, you first override the onCreateDialog() method in the Activity class
@Override
protected
Dialog onCreateDialog(int id) {
...
}
This method is called when you call the showDialog() method
This method is called when you call the showDialog() method
btnShow_Dialog = (Button)
findViewById(R.id.btnShow_Dialog);
btnShow_Dialog.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showDialog(0);
}
});
Download source code: updating...
Đăng ký:
Nhận xét (Atom)
Thông báo lỗi !!!
Nếu click vào bài viết mà chuyển sang website khác bạn vui lòng chờ 5s sau đó click skip Ad để vào bài viết nhé. Cảm ơn!
Xem nhiều tuần qua
-
Removable Disk xảy ra trong trường hợp usb của bạn sắp hỏng hoặc nhiễm virut. Hoặc trong trường hợp bạn copy dữ liệu vào trong usb có chứa ...
-
Thông thường ở chế độ mặc định các item (hay các dòng) trong ListView chỉ hiển thị các dòng text. Để tùy biến các item của ListView trông ...
-
Một thể loại game kinh điển rắn săn mồi được xây dựng trên nền tảng C++ rất thú vị cho các bạn đang nghiên cứu lập trình trên C++. Game đ...
-
Kho tài liệu lập trình android đầy đủ phiên bản Tiếng Anh dành cho bạn nào muốn tìm hiểu về lập trình android. Bộ tài liệu này bao gồm tài l...
-
Cách kết bạn GooglePlus nhanh, có người share rồi nhưng mình vẫn muốn share lại vì LÀM THÌ DỄ, nhưng LÀM CÓ HIỆU QUẢ mới khó. HƯỚNG DẪN: ...
-
1. Create a New Android Application Project 2. Creating the layout of the main We are going to make a very simple layout xml for t...
-
Share ebook học lập trình C từ cơ bản đến nâng cao cực hay Mô tả: -Title The C Programming Language, 2nd Edition -Author(s) Brian W. ...
-
XML stands for Extensible Mark-up Language.XML is a very popular format and commonly used for sharing data on the internet. This chapter ex...
-
Hiện nay, tiếng Anh được coi là ngôn ngữ quốc tế số một trên thế giới. Hàng triệu người từ các nền văn hóa khác nhau đều nỗ lực học tiếng A...
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 là thế hệ kế tiếp của hệ điều hành Windows Server, có thể giúp các chuyên gia công nghệ thông tin có thể ki...
Followers
Like us on facebook
Được tạo bởi Blogger.
Total Pageviews
Giới thiệu về tôi
Registry to earn $50 now. !!!
Copyright © 2011 programming share. All Rights Reserved.
Designed by Free Blogger Templates and Blogger Teacher - Berita Selebriti - friable vs non-friable asbestos
Powered by Blogger.
Designed by Free Blogger Templates and Blogger Teacher - Berita Selebriti - friable vs non-friable asbestos
Powered by Blogger.